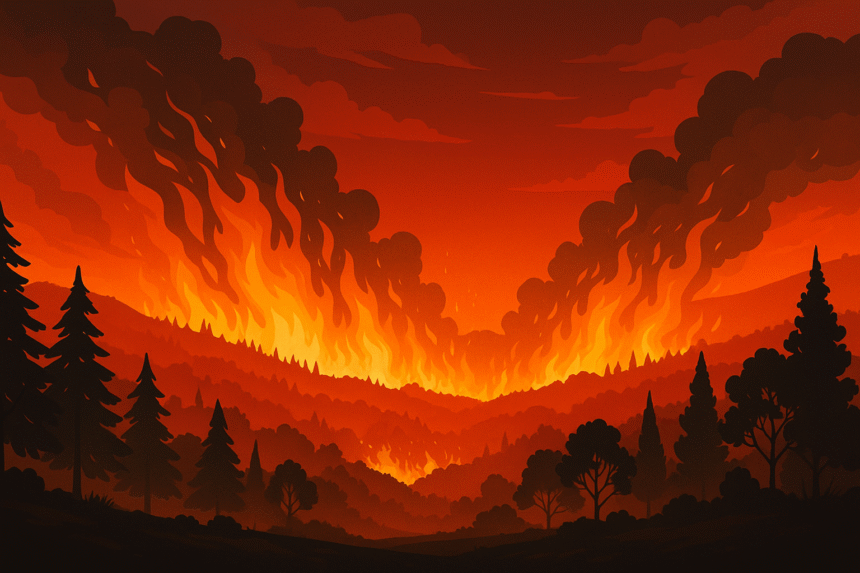
Southern France and parts of southern Europe are facing one of the most severe wildfire outbreaks in recent history. Fueled by extreme temperatures and persistent drought, the fires have consumed an area larger than Paris, causing widespread destruction and displacing thousands.
According to the French Interior Ministry, the fires have resulted in the death of at least one individual, while several others — including civilians and firefighters — have sustained injuries. Authorities report that some people remain missing, and search-and-rescue operations are ongoing.
Emergency response teams have mobilized more than 2,000 personnel and 30 firefighting aircraft, including Canadair water bombers, to combat the fires in the heavily affected regions of Provence and Occitanie. Entire towns have been evacuated, with officials warning that conditions could worsen due to strong winds and high temperatures.
French Prime Minister Élisabeth Borne described the situation as “a disaster without precedent.” In a press briefing, she emphasized the government’s commitment to safeguarding lives and property but acknowledged the extraordinary scale of the crisis.
The impact of the fires extends beyond France. In southern Spain, wildfires have erupted in Tarifa and Algeciras, forcing evacuations and disrupting transportation. Spanish firefighting units are working around the clock as hundreds of hectares of land have been consumed.
Meteorologists have linked the intensity of the fires to ongoing heatwaves, with temperatures exceeding 45°C (113°F) in parts of the region. The combination of extreme heat, dry vegetation, and strong winds has created ideal conditions for fire outbreaks.
Climate experts warn that such events are becoming more common due to global warming. The European Commission has activated its Emergency Response Coordination Centre (ERCC) to provide cross-border support, and several EU countries have already pledged assistance.
Environmental organizations are urging European governments to implement long-term solutions to mitigate wildfire risks. Recommendations include improved forest management, investment in early-warning systems, and stronger climate resilience strategies.
As efforts continue to contain the blazes, authorities caution that the crisis is far from over. With temperatures expected to remain dangerously high, the region remains on high alert.